Example 7.15: Predicting Electron-pair Geometry and Molecular Structure: \(\ce{XeF4}\)
Of all the noble gases, xenon is the most reactive, frequently reacting with elements such as oxygen and fluorine. Predict the electron-pair geometry and molecular structure of the \(\ce{XeF4}\) molecule.Solution
The Lewis structure of \(\ce{XeF4}\) indicates six regions of high electron density around the xenon atom: two lone pairs and four bonds: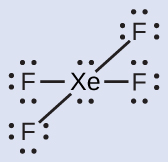
These six regions adopt an octahedral arrangement (panel A below), which is the electron-pair geometry. To minimize repulsions, the lone pairs should be on opposite sides of the central atom. The five atoms are all in the same plane and have a square planar molecular structure (panel B below).
