Example 9.3: Calculation of Pressure Using a Closed-End Manometer
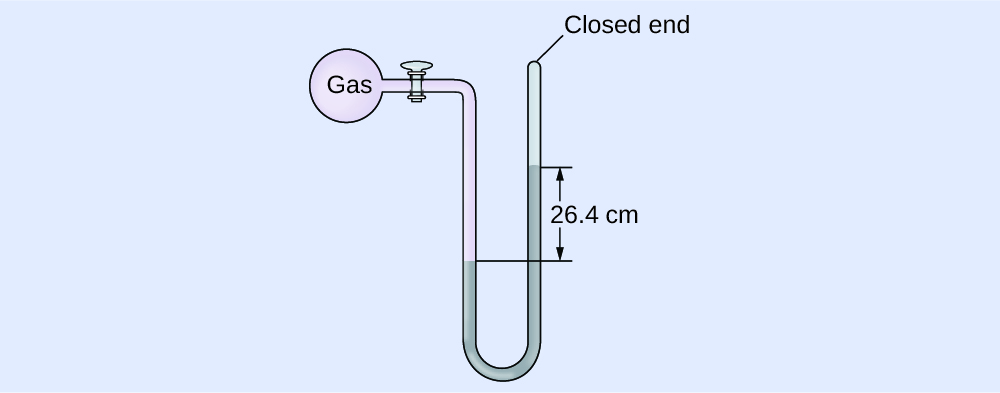
The pressure of a sample of gas is measured with a closed-end manometer, as shown below. The liquid in the manometer is mercury. Determine the pressure of the gas in:(a) torr
(b) Pa
(c) atm
Solution
The pressure of the gas is equal to a column of mercury of height 26.4 cm. (The pressure at the bottom horizontal line is equal on both sides of the tube. The pressure on the left is due to the gas and the pressure on the right is due to 26.4 cm Hg, or mercury.) We could use the equation \(p = \mathrm{hρg}\) as in Example 1, but it is simpler to just convert between units using Table 1.\(P_{\mathrm{gas}}\) \(= 264.\ \mathrm{mmHg}\)
\(P_{\mathrm{gas}}\) \(= 264.\ \mathrm{mmHg}\)
\(\ \ \ =264.\ \mathrm{torr}\)
\(P_{\mathrm{gas}}\) \(= 264.\ \mathrm{torr}\)
\(\ \ \ =3.52\times 10^{4}\ \mathrm{Pa}\)
\(P_{\mathrm{gas}}\) \(= 3.52\times 10^{4}\ \mathrm{Pa}\)
\(\ \ \ =0.347\ \mathrm{atm}\)