Example 9.19: Volume of Gaseous Product
What volume of hydrogen at 27 °C and 723 torr may be prepared by the reaction of 8.88 g of gallium with an excess of hydrochloric acid?\(\ce{2Ga(s)}\)\(\ce{ + }\)\(\ce{6HCl(aq)}\)\(\ce{->}\)\(\ce{2GaCl3(aq)}\)\(\ce{ + }\)\(\ce{3H2(g)}\)\(\ce{ }\)
Solution
\(T_{\mathrm{gas}}\) \(= 27.\ \mathrm{°aC}\)\(P_{\mathrm{gas}}\) \(= 723.\ \mathrm{torr}\)
\(m_{\mathrm{\ce{Ga}}}\) \(= 8.88\ \mathrm{g}\)
To convert from the mass of gallium to the volume of \(\ce{H2(g)}\), we need to do something like this:
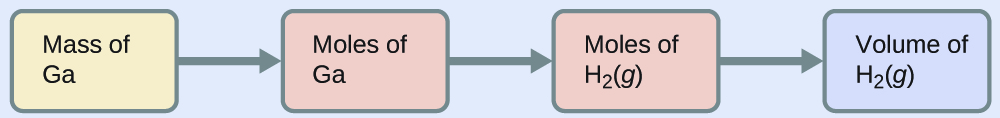
\(ν_{\mathrm{\ce{Ga(s)}}}\) \(= 2\)
\(ν_{\mathrm{\ce{H2(g)}}}\) \(= 3\)
\(V_{\mathrm{gas}}\) = ?
\(n_{\mathrm{\ce{Ga}}}\) \(= \dfrac{m_{\mathrm{\ce{Ga}}}}{M_{\mathrm{\ce{Ga}}}}\)
\(\ \ \ =\dfrac{8.88\ \mathrm{g}}{69.723\ \frac{\mathrm{g}}{\mathrm{mol}}}\)
\(\ \ \ =0.1274\ \mathrm{mol}\)
\(n_{\mathrm{\ce{H2}}}\) \(= n_{\mathrm{\ce{Ga}}} \cdot \dfrac{ν_{\mathrm{\ce{H2(g)}}}}{ν_{\mathrm{\ce{Ga(s)}}}}\)
\(\ \ \ =0.1274\ \mathrm{mol} \cdot \dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(\ \ \ =0.1274\ \mathrm{mol} \cdot \frac{3 }{ 2}\)
\(\ \ \ =0.1910\ \mathrm{mol}\)
\(P_{\mathrm{gas}} \cdot V_{\mathrm{gas}} = n_{\mathrm{gas}} \cdot R \cdot T_{\mathrm{gas}}\)
\(R\) \(= 8.314\ \frac{\mathrm{J}}{\mathrm{mol}\ \mathrm{K}}\)
\(V_{\mathrm{gas}}\) \(= \dfrac{n_{\mathrm{\ce{H2}}} \cdot R \cdot T_{\mathrm{gas}}}{P_{\mathrm{gas}}}\)
\(\ \ \ =\dfrac{0.1910\ \mathrm{mol} \cdot 8.314\ \frac{\mathrm{J}}{\mathrm{mol}\ \mathrm{K}} \cdot 27.\ \mathrm{°aC}}{723.\ \mathrm{torr}}\)
\(\ \ \ =\dfrac{1.5883\ \frac{\mathrm{J}}{\mathrm{K}} \cdot 300.\ \mathrm{K}}{723.\ \mathrm{torr}}\)
\(\ \ \ =\dfrac{476.7\ \mathrm{J}}{723.\ \mathrm{torr}}\)
\(\ \ \ =4.95\times 10^{-3}\ \mathrm{m}^{3}\)
Then, we can use the ideal gas law: